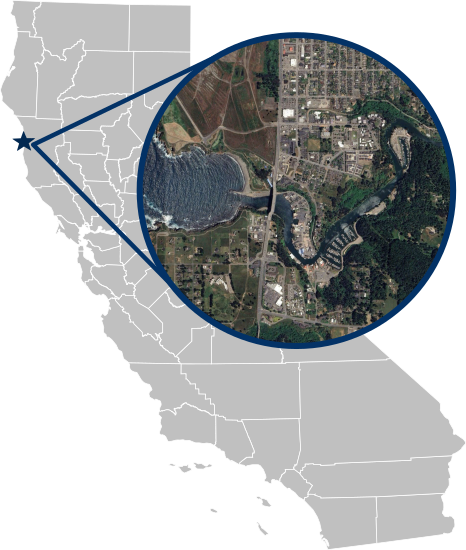
The Noyo River estuary, located on California's rugged North Coast near Fort Bragg, flows approximately 41 miles from its headwaters in the Mendocino Range to the Pacific Ocean. Draining a watershed of roughly 113 square miles, the river receives an average of 40 to 60 inches of annual rainfall, concentrated during the winter months. The estuary, which spans about 3 miles, supports diverse habitats including riparian zones, tidal flats, and marshes, serving as critical habitat for coho salmon and steelhead trout.
Unlike some nearby systems, the mouth of the Noyo River typically remains open year-round due to the river’s consistent flow and tidal influence, ensuring connectivity between freshwater and marine environments. Real-time water level monitoring at the Noyo River provides valuable data on tidal dynamics, sediment transport, and flooding risks, while supporting conservation and management efforts for this ecologically and economically significant estuary.
This site is in collaboration with the Noyo Center for Marine Science.
